Opting Out of Data Brokers for Businesses Safeguarding Corporate Data
페이지 정보
작성자 Shelby 작성일24-07-09 14:40 조회201회 댓글0건관련링크
본문

In the contemporary digital landscape, the management of proprietary and confidential information has become a paramount concern for organizations worldwide. This section delves into the critical strategies that companies can employ to shield their sensitive data from external entities, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of their operations. The focus here is on proactive measures that can be implemented to fortify the security of corporate assets in an era where data breaches are increasingly prevalent.
Understanding the Risks: Every day, businesses are exposed to numerous threats that aim to exploit their valuable data. These threats can originate from various sources, including unauthorized access to company records, malicious software, and the actions of unscrupulous individuals or groups. It is essential for enterprises to recognize these risks and develop robust protocols to mitigate them.
Protecting Sensitive Information: The cornerstone of any effective strategy involves the careful handling and protection of sensitive information. This includes not only financial records and intellectual property but also employee and customer details. By adopting stringent data management practices, companies can significantly reduce the likelihood of their information falling into the wrong hands.
Moreover, the implementation of advanced cybersecurity measures is crucial. These can range from sophisticated encryption techniques to regular audits of security systems. Additionally, fostering a culture of vigilance within the organization, where every employee is aware of their role in safeguarding company data, can be a powerful deterrent against potential threats.
In conclusion, the proactive defense of corporate information is not just a compliance requirement but a strategic imperative for the longevity and success of any business. By embracing these principles, organizations can navigate the complex digital terrain with confidence, ensuring the protection of their most valuable assets.
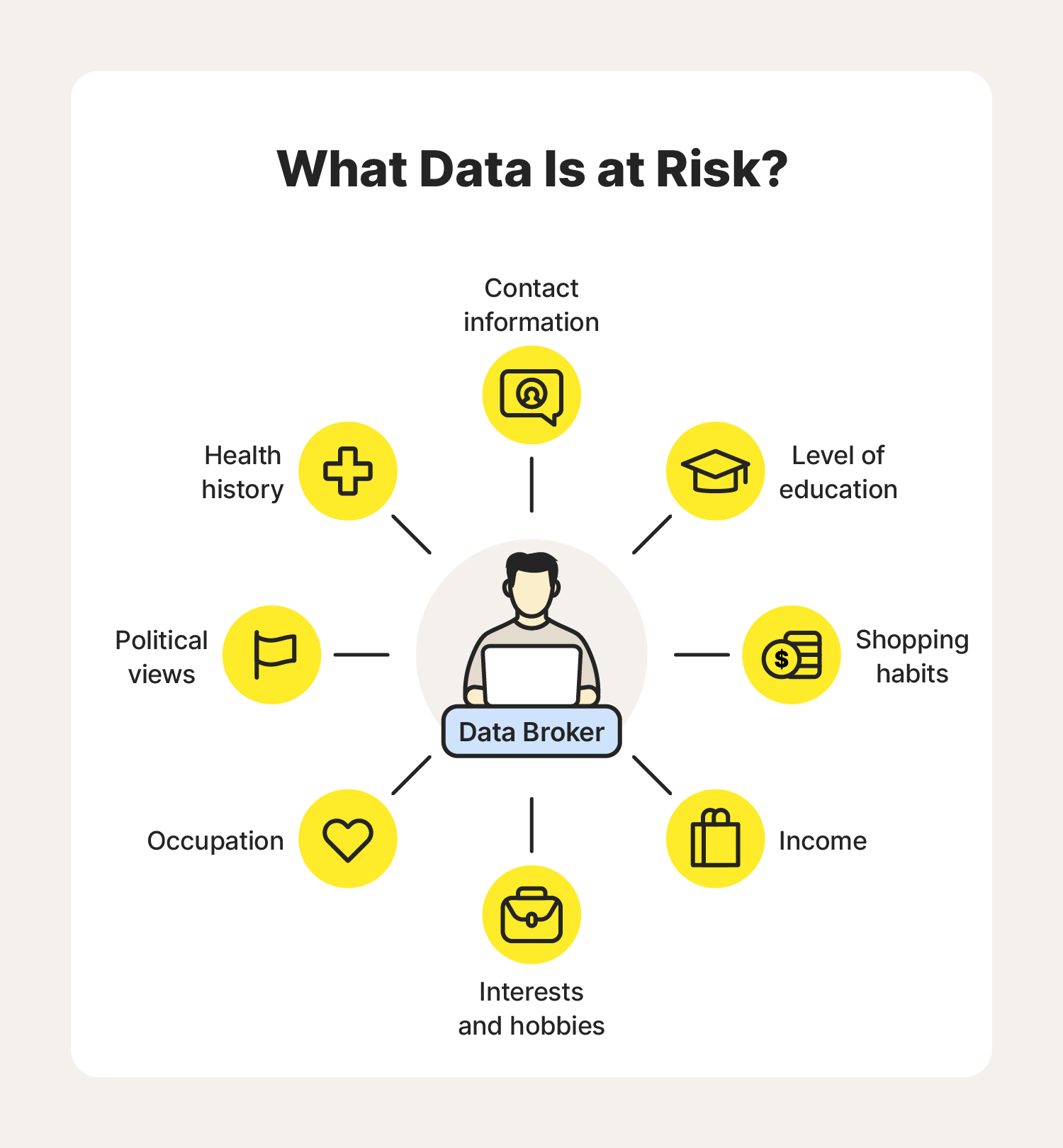
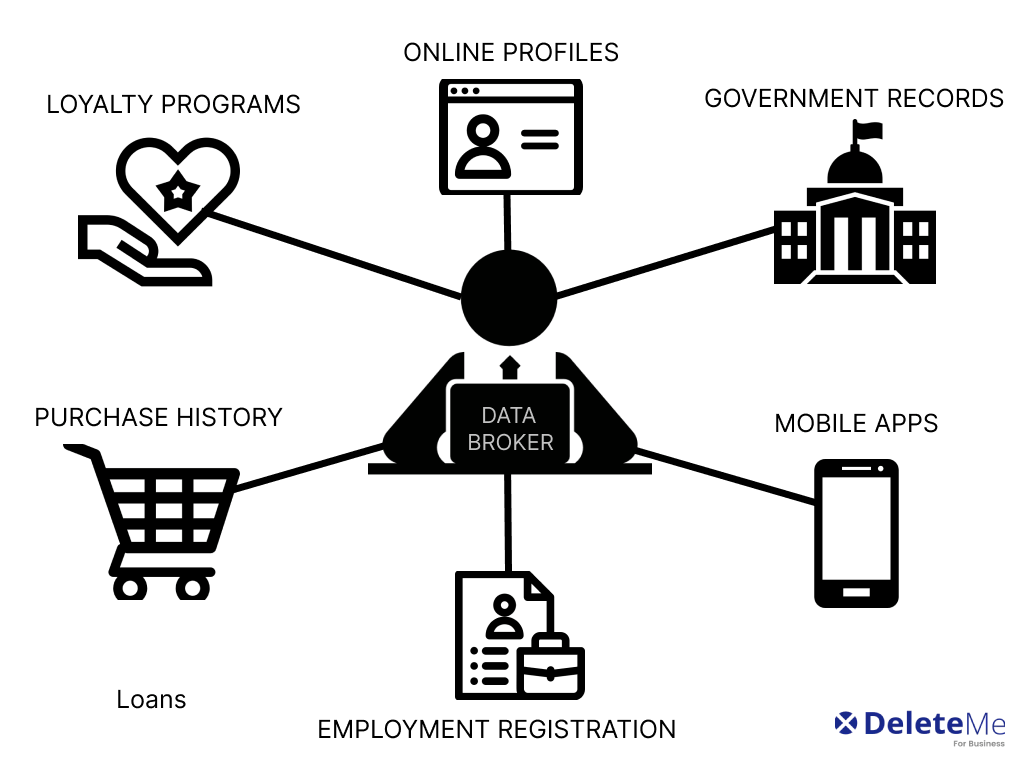
Understanding Data Brokers and Their Impact
This section delves into the complex world of information intermediaries and their profound influence on the digital landscape. These entities play a crucial role in the collection, aggregation, and distribution of vast amounts of user details across various platforms. Understanding their operations and the implications of their activities is essential for maintaining control over sensitive details and ensuring the integrity of digital security measures.
The Role of Information Intermediaries: Often operating behind the scenes, these entities gather and compile user data from numerous sources. This data might include basic identifiers such as names and addresses, but can also extend to more sensitive information like financial records or browsing histories. The primary function of these intermediaries is to provide this aggregated data to other businesses, which use it for marketing, analytics, and other commercial purposes.
Impact on Digital Privacy: The activities of information intermediaries have significant repercussions on individual privacy. By collecting and disseminating personal details, they can inadvertently expose individuals to risks such as identity theft or targeted advertising. Moreover, the lack of transparency in their operations often means that individuals are unaware of how their information is being used or shared.
Regulatory Frameworks: Recognizing the potential threats posed by these intermediaries, various regulatory bodies have implemented frameworks aimed at curbing their more invasive practices. These regulations typically focus on enhancing transparency and giving individuals more control over their personal details. Compliance with these frameworks is crucial not only for the intermediaries themselves but also for the businesses that rely on their services.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of information intermediaries is vital for anyone concerned with digital privacy and security. By comprehending their methods and the legal constraints under which they operate, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against the potential pitfalls associated with the widespread dissemination of personal details.
The Legal Landscape of Data Privacy
In this section, we delve into the complex realm of legal frameworks that govern the protection of sensitive details. Understanding these regulations is crucial for organizations aiming to maintain compliance and uphold the integrity of their confidential information.
Legislation and Regulations: Numerous laws and directives have been established globally to safeguard individual and organizational secrets. These include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which imposes stringent requirements on how entities handle and process private data. Similarly, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States provides residents with enhanced rights over their personal details.
Compliance Challenges: Navigating these legal landscapes can be daunting, as they often require detailed knowledge of both local and international laws. Organizations must ensure they are not only aware of these regulations but also actively implementing policies and procedures that align with them.
Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to adhere to these legal requirements can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and damage to an organization's reputation. It is imperative for companies to regularly review and update their practices to avoid such consequences.
Strategic Approaches: To effectively manage this legal terrain, organizations should consider employing dedicated teams or consultants who specialize in privacy law. These experts can help tailor strategies that mitigate risks and ensure ongoing compliance.
In conclusion, the legal landscape of privacy is a critical aspect that organizations cannot afford to overlook. By staying informed and proactive, companies can protect their interests and maintain the trust of their stakeholders.
Strategies for Opting Out of Data Broker Lists
This section delves into effective methods to disassociate from entities that aggregate and distribute sensitive organizational details. It is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of proprietary information. By implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and misuse of their valuable assets.
To effectively remove your organization's information from these lists, it is essential to follow a structured approach. Below is a table outlining key steps and considerations:
| Step | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Identify Entities | Determine which organizations collect and sell your data. | Conduct research to compile a list of such entities. |
| Review Policies | Understand the removal policies of each entity. | Visit their websites or contact them directly for policy details. |
| Initiate Removal | Request the removal of your data from their databases. | Follow the specified procedures, which may include filling opt out from White Pages online forms or sending emails. |
| Monitor Compliance | Ensure that the entities comply with your removal request. | Regularly check to confirm that your data is no longer accessible through them. |
| Update Practices | Implement internal changes to prevent future inclusion. | Review and update data handling and sharing policies within your organization. |
By systematically following these steps, organizations can significantly enhance their control over the dissemination of their proprietary information. It is important to remain vigilant and proactive in managing these relationships to protect the organization's reputation and assets.
Implementing Robust Cybersecurity Measures
In this section, we delve into the critical steps organizations must take to fortify their digital defenses. The focus here is on enhancing the security infrastructure to protect sensitive details and ensure the integrity of operations in the digital realm.
Encryption plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive details within organizations. By converting data into a code that can only be accessed with a specific decryption key, encryption effectively prevents unauthorized access. This method is particularly crucial for protecting information during transmission and storage.
Key Management is another essential aspect of robust cybersecurity. Organizations must implement strict protocols for generating, distributing, and storing encryption keys. Effective key management ensures that only authorized personnel can access the keys, thereby maintaining the confidentiality of encrypted data.
Furthermore, integrating advanced authentication methods such as two-factor authentication (2FA) and biometrics can significantly enhance security. These methods add layers of verification, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive systems or data.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are also vital components of a robust cybersecurity strategy. These practices help identify vulnerabilities and test the effectiveness of security measures, allowing organizations to address gaps before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
Finally, fostering a culture of security awareness among employees is crucial. Regular training sessions can educate staff about the latest threats and best practices for maintaining security, ensuring that everyone in the organization plays a role in protecting sensitive information.
The Role of Encryption in Protecting Corporate Data
In the realm of digital security, one of the most potent tools at our disposal is encryption. This section delves into how encryption serves as a critical component in fortifying the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information within organizations. By transforming data into a form that can only be accessed by authorized users, encryption plays a pivotal role in thwarting unauthorized access and ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unintelligible to those without the correct decryption keys.
Encryption is not merely a technical solution; it is a strategic imperative that helps organizations maintain compliance with various regulatory standards and enhances overall trust in digital transactions. Below are several key aspects of how encryption safeguards sensitive information:
- Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that only intended recipients can understand the information, thereby maintaining confidentiality.
- Integrity: By encrypting data, organizations can verify that it has not been altered in transit, ensuring its integrity.
- Authentication: Encryption methods often include authentication mechanisms that verify the identity of the communicating parties.
- Non-repudiation: Encryption can provide proof that a message was sent and received, which is crucial in legal and compliance contexts.
Implementing robust encryption practices involves several steps and considerations. Here is a list of strategies to effectively integrate encryption into your organization's security framework:
- Choose appropriate encryption algorithms that are robust and widely accepted in the industry.
- Regularly update encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access through compromised keys.
- Use secure key management practices to ensure that keys are stored and handled securely.
- Incorporate encryption into all aspects of data handling, from storage to transmission.
- Educate staff about the importance of encryption and the proper protocols for its use.
In conclusion, encryption is a foundational element of any comprehensive security strategy. By understanding and implementing effective encryption practices, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to protect sensitive information from a myriad of threats in the digital landscape.
Employee Training: A Key to Data Security
In the intricate landscape of maintaining organizational integrity, the role of staff education cannot be overstated. It is through comprehensive training programs that companies can fortify their defenses against potential breaches and ensure that all team members are equipped with the knowledge necessary to uphold stringent security protocols.
Effective training initiatives should cover a broad spectrum of topics, ensuring that every employee understands their role in protecting sensitive assets. Here are several critical components that should be included in any robust training program:
- Understanding Threats: Employees must be educated on the various types of threats they might encounter, including phishing, malware, and social engineering tactics.
- Security Protocols: Detailed instruction on the organization's security policies and procedures, including password management, secure data handling, and incident reporting.
- Role-Specific Training: Tailored training that addresses the unique security responsibilities of different roles within the organization.
- Regular Updates: Continuous learning opportunities to stay abreast of evolving security challenges and updates to organizational policies.
- Hands-On Practice: Practical exercises that simulate real-world scenarios, enhancing the ability to respond effectively to security incidents.
Implementing a comprehensive training program not only enhances the security posture of an organization but also fosters a culture of vigilance and responsibility. Employees who are well-informed are less likely to inadvertently compromise security measures and are more capable of identifying and mitigating potential threats.
Moreover, regular audits and feedback mechanisms should be integrated into the training framework to ensure continuous improvement. This iterative approach ensures that the training remains relevant and effective, adapting to new challenges and changes in the security landscape.
In conclusion, investing in employee training is a strategic move that significantly enhances an organization's ability to protect its critical assets. By empowering employees with the knowledge and skills to uphold security standards, organizations can build a resilient defense against the ever-evolving array of security threats.
Auditing Data Practices for Compliance
Ensuring adherence to regulatory standards is a critical aspect of managing sensitive digital assets. This section delves into the importance of systematic reviews of operational protocols to maintain alignment with legal requirements and industry best practices.
Regular assessments are essential in identifying gaps in security measures and operational procedures. These evaluations help organizations pinpoint areas that may be vulnerable to breaches or non-compliance with prevailing laws.
Compliance audits typically involve a thorough examination of internal processes, including access controls, data handling, and encryption protocols. The goal is to verify that all practices meet the necessary standards set by governing bodies.
Implementing a robust auditing framework not only aids in compliance but also enhances overall security posture. It provides a clear picture of the organization's strengths and weaknesses, guiding strategic decisions on resource allocation and policy updates.
Moreover, these audits serve as a proactive measure against potential threats, ensuring that the organization is well-prepared to handle any security challenges. Regular reviews also foster a culture of accountability and continuous improvement within the organization.
In conclusion, integrating regular audits into the operational routine is crucial for maintaining a secure and compliant environment. It is a proactive step towards protecting valuable digital assets and ensuring the organization's resilience against evolving threats.
The Importance of Regular Data Privacy Reviews
In the contemporary digital landscape, the systematic evaluation of information protection protocols is paramount. This section delves into the criticality of maintaining periodic assessments to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive details.
Regular reviews are essential in identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that all security measures are up-to-date and effective. These evaluations help organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and comply with stringent regulations governing the handling of sensitive data.
Key components of these reviews include assessing the robustness of existing security protocols, verifying compliance with industry standards, and identifying areas for improvement. By conducting these assessments, organizations can proactively address potential risks and enhance their overall security posture.
Moreover, regular reviews foster a culture of vigilance and continuous improvement within the organization. They empower employees at all levels to understand their roles in protecting sensitive information and to take proactive steps to mitigate risks.
In conclusion, the practice of regular data privacy reviews is not just a regulatory necessity but a strategic imperative for any organization aiming to protect its valuable information assets and maintain stakeholder trust.
Leveraging Technology to Safeguard Information
In this section, we delve into real-world examples that highlight effective strategies employed by various entities to protect sensitive data. These case studies not only demonstrate the practical application of advanced security measures but also underscore the importance of a proactive approach in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of critical information.
Case Study 1: The Financial Institution's Proactive Security Measures
A prominent financial institution implemented a comprehensive security framework that included state-of-the-art encryption techniques and regular security audits. By integrating these measures, the institution significantly reduced the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, thereby enhancing trust among its clients and stakeholders.
Case Study 2: The Healthcare Provider's Data Protection Strategy
A leading healthcare provider adopted a stringent data protection policy that involved continuous monitoring and the use of advanced analytics to detect and prevent potential threats. This approach not only safeguarded patient records but also ensured compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, thus maintaining the provider's reputation and credibility.
Case Study 3: The Tech Company's Innovative Security Solutions
A tech giant revolutionized its security protocols by developing proprietary software that utilizes artificial intelligence to predict and mitigate cyber threats. This innovative solution has not only protected the company's intellectual property but also set a new industry standard for data security.
These case studies illustrate the diverse strategies that organizations can employ to fortify their defenses against cyber threats. By learning from these successful implementations, entities across various sectors can enhance their own security measures and better protect their valuable information assets.
Case Studies: Successful Corporate Data Privacy Strategies
This section delves into real-world examples that showcase effective approaches adopted by various entities to enhance the security of their sensitive records. By examining these instances, readers can gain insights into practical methods that have proven successful in protecting critical organizational assets from unauthorized access and breaches.
One notable case study involves a multinational corporation that implemented a comprehensive training program for all its staff. This initiative focused on educating employees about the importance of maintaining the confidentiality of internal documents and the correct protocols for handling such information. The program not only reduced the number of inadvertent leaks but also fostered a culture of vigilance and responsibility among the workforce.
Another compelling example is a tech firm that leveraged advanced encryption technologies to safeguard its proprietary software. By integrating robust cryptographic solutions into their data management systems, the company was able to significantly enhance the protection of their intellectual property, thereby thwarting potential cyber-attacks and espionage attempts.
A third case highlights a financial institution that regularly conducts thorough audits of its data handling practices. This proactive approach ensures that all procedures align with the latest regulatory standards and industry best practices. The institution's commitment to continuous improvement has not only bolstered its reputation for reliability but also minimized the risk of regulatory penalties.
These case studies underscore the importance of a multifaceted approach to securing sensitive organizational data. They demonstrate that a combination of employee education, technological innovation, and rigorous compliance checks can create a robust defense against the myriad threats that organizations face in the digital age.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.